

After importation in 1928 of a Boeing 69-B (F2B-1) by the Imperial Navy, and, in the following year, the fourth Boeing 100 (essentially similar to the F4B-1), the two aircraft were shown to industry as examples of the then-current US shipboard fighter technology. Nakajima, which had previously built the Gloster Gambet (A1N1-2) for the Imperial Navy, initiated development of a carrier fighter based broadly on the Boeing design as a private venture. Responsibility for the fighter was assigned to Takao Yoshida and two prototypes powered by the Jupiter Vi engine were completed in December 1929. Evaluated by the Navy in the following year, these prototypes were rejected as they were considered to offer an insufficient improvement over the A1N1. Some redesign was undertaken by Jingo Kurihara, and with a 580 hp Kotobuki 2 engine, a further prototype was completed in May 1931. Another prototype followed later in 1931, the type then being adopted by the Navy in April 1932 as the A2N1 (Type 90). The aircraft had a fabric-covered metal fuselage and a similarly skinned wing of mixed construction. The principal production version was the A2N2 (Type 90-III) differing in having five degrees of dihedral on the upper wing main panels. Series production was undertaken from 1932 until 1936 by both the parent company and Sasebo, about 100 Type 90 fighters being manufactured in three models (I-III). The A3N1 was a two-seat training derivate of which 66 were produced between 1936 and 1939.
The Nakajima A1N was used on the carriers Hosho, Kaga and Ryujo. It was also used by the Kure Kokutai.
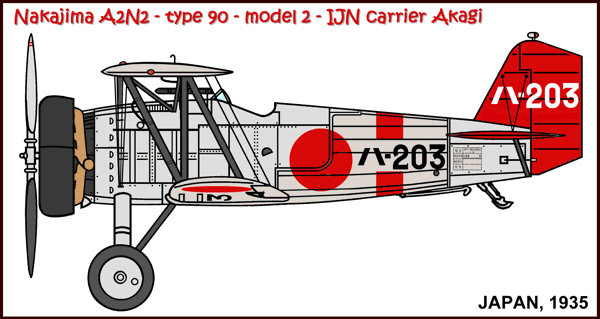
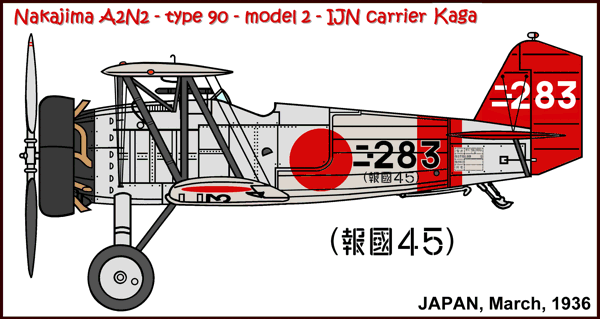
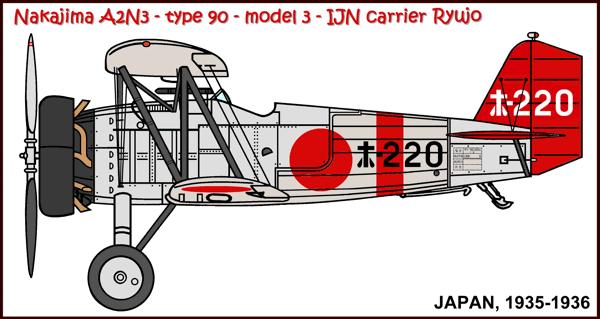
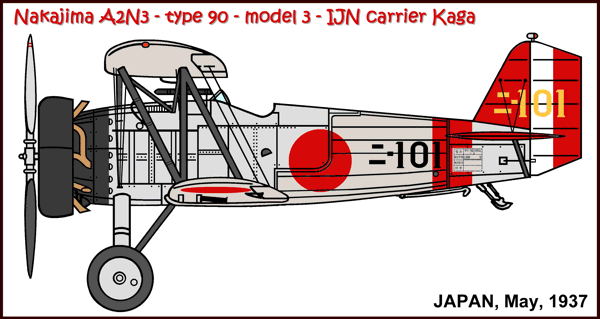
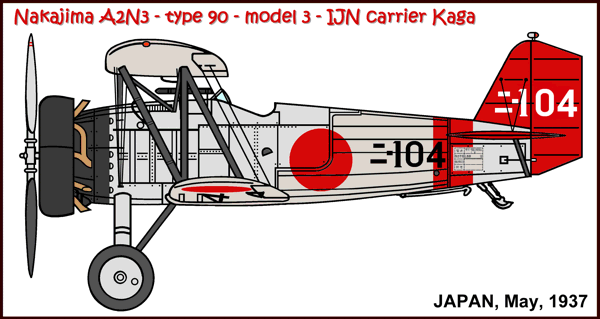
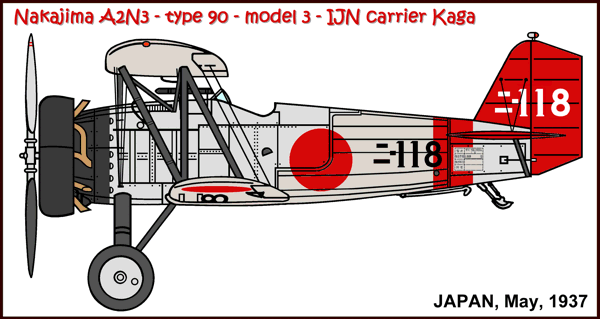
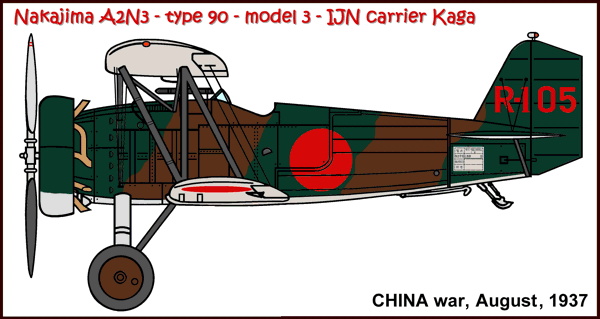
Versions (with no. built):
A2N (4) – Prototypes.
A2N1
A2N2
A2N3
The Nakajima A2N saw service in: Japan (IJNAF).
Total production: 106
Technical details Nakajima A2N1
Type:____________Fighter
Crew:____________1
Span:____________9.37 m
Lenght:__________6.18 m
Engine:__________Nakajima Kotobuki 2 / 450 hp)
Max speed:_______293 km/h at 3000 m
Service ceiling:_7000 m
Armament:________2x7.7 mm fixed forward firing machine guns
Sources:
Japanese Naval Aces and Fighter Units in World War II - Ikuhiko Hata and Yasuho Izawa, translated by Don Cyril Gorham, 1989 United States Naval Institute, Annapolis, ISBN 0-87021-315-6
The Complete Book of Fighters - William Green and Gordon Swanborough, Greenwich Editions, London, ISBN 0-86288-220-6
Additional information and images kindly provided by Sidnei E. Maneta.


